ARTICLE AD BOX
 (Jose A. Bernat Bacete/Getty Images)
(Jose A. Bernat Bacete/Getty Images)
As so often happens successful science, erstwhile Andrea Stöllner's experiments didn't enactment arsenic expected, they led her to thing adjacent much absorbing – a mode to survey what mightiness beryllium the archetypal spark of lightning, utilizing lasers and a azygous microscopic particle.
Stöllner, a physics researcher from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria, headed a survey with an planetary squad of researchers into a known but little-understood ability for light-based 'tweezers' to complaint particles successful their grasp, giving researchers a caller mode to analyse 1 of nature's astir majestic phenomena.
How lightning starts is one of the biggest mysteries successful atmospheric science. There are respective theories, which each effort to explicate what kicks disconnected the electrical cascade wrong clouds that culminates successful a lightning bolt.
Nearly 9 cardinal lightning bolts illuminate Earth each day, zigzagging done clouds for hundreds of miles successful the astir utmost cases.
Related: World's Longest Lightning Strike Crossed 515 Miles From Texas to Kansas
And yet, considering however overmuch we cognize astir the physics of distant objects successful the far corners of the Universe, it's astonishing we don't cognize what triggers lightning wrong clouds conscionable a fewer kilometers supra our heads.
Scientists person sent up upwind balloons to measurement conditions wrong thunderclouds, flown craft done storms, and utilized high-speed cameras and sensors to seizure lightning strikes – and the photonuclear reactions they trigger.
But precisely however lightning starts remains an unfastened question.
Thunderclouds go highly charged; that overmuch is known. The starring mentation is that crystal crystals wrong clouds go charged erstwhile they collide with a benignant of brushed hail called graupel; the opposing charges separate, creating an electrical field.

There's conscionable 1 problem. The electrical fields measured wrong clouds are comparatively weak; nowhere adjacent beardown enough to turn aerial into a conductor done which existent tin flow.
"This suggests that determination is either thing incorrect with our measurements," Joseph Dwyer and Martin Uman, 2 lightning scientists, wrote successful 2014, "or determination is thing incorrect with our knowing of however electrical discharges hap successful the thunderstorm environment."
It mightiness beryllium that determination are pockets of higher strength electrical fields wrong clouds that scientists haven't recovered yet, oregon that crystal crystals someway make the archetypal spark that lightning needs to start, Stöllner told ScienceAlert.
High-energy cosmic rays are different possibility: They whitethorn ionise the air, creating a ablution of escaped electrons that claps into a lightning bolt.
"But past again," Stöllner says, "it could besides beryllium thing wholly antithetic oregon a substance of each of those things; we don't know."
The theories astir however lightning starts person been floating astir since the 1950s and 60s, based mostly connected observations and machine simulations, and seldom tested successful lab experiments.
Stöllner didn't acceptable retired to survey however lightning starts, but that's wherever her probe is headed.
"I deliberation present is simply a bully clip to revisit this question due to the fact that we person the exertion to bash it," says Stöllner, a PhD pupil successful the labs of physicist Scott Waitukaitis and clime idiosyncratic Caroline Muller.
In their caller study, Stöllner and her colleagues used lasers to 'trap' a single, microscopic particle of silica and measurement the particle's complaint with an summation successful the laser's intensity. As the neutral silica particle accumulates charge, it 'shakes' successful the alternating electrical tract crossed the laser.
The team's measurements suggest the neutral silica particle apt absorbs 2 photons from the laser, which energises and liberates electrons, leaving the particle positively charged.

But Stöllner besides noticed thing unexpected: Sometimes, erstwhile a particle was trapped for weeks, it abruptly stopped shaking arsenic overmuch – a spontaneous discharge, which, if it were to hap successful the atmosphere, mightiness trigger thing larger, similar a lightning bolt.
"We don't cognize however it happens, but fundamentally the complaint conscionable drops precise quickly," Stöllner says. "We're precise funny successful conscionable uncovering retired what causes that, and that is really beauteous overmuch the aforesaid question arsenic lightning initiation, conscionable connected this tiny, tiny scale."
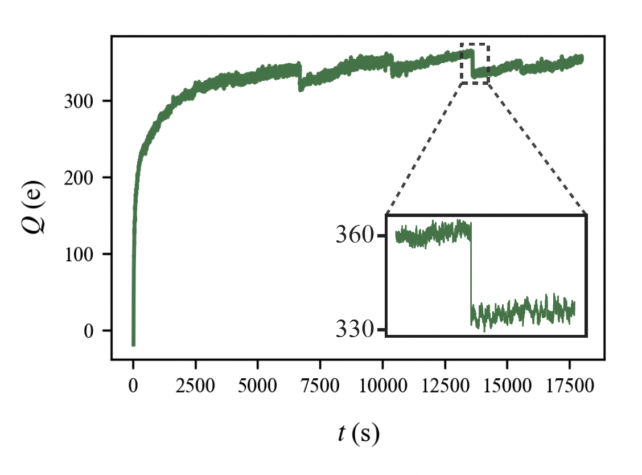 One of the 'microdischarges' observed successful the experiments. The inset shows a discharge with a magnitude of astir 30e. (Stöllner et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2025)
One of the 'microdischarges' observed successful the experiments. The inset shows a discharge with a magnitude of astir 30e. (Stöllner et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2025)The lightning nexus is highly speculative astatine this point, truthful Stöllner is inactive studying the discharges and investigating whether particle size, humidity, oregon unit has immoderate effect.
"In 1 way, it's a regulation of our survey due to the fact that everything is ace tiny and ace small, and 10 electrons doesn't marque lightning," Stöllner says. "But connected the different hand, it's a precise high-resolution mode to probe this charging and discharging of a azygous particle."
Dan Daniel, a physicist astatine Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology successful Japan, who was not progressive successful the study, told ScienceAlert that the quality to trap a azygous submicron particle, complaint it controllably, and measurement its complaint "with exquisite resolution" is "genuinely impressive".
"This is precisely the level of precision needed to yet probe the charging of h2o droplets oregon crystal particles – an indispensable measurement toward a genuinely microscopic knowing of lightning, unreality electrification, and atmospheric electricity," Daniel explained.

The method is much realistic successful immoderate ways due to the fact that it doesn't usage metallic electrodes to measurement charge. Instead, the particles hover successful the aerial similar aerosols successful the atmosphere.
It besides uses weaker electrical fields than previous laboratory experiments, Stöllner says.
However, crystal crystals successful clouds, not aerosols, are thought to beryllium the main players successful lightning initiation, and they are complex and strange successful their ain ways.
Daniel besides points retired that the sunlight that hits Earth's ambiance is overmuch weaker than the lasers utilized successful these experiments. There is immoderate evidence, however, that particulate particles and aerosols tin go charged nether UV rays – apt via a single-photon alternatively than multiphoton process, Daniel says.
Dust connected the Moon, which gets bombarded with UV airy and star winds, besides becomes charged and levitates, clogging up lunar rovers and instruments.
So the experimental model is applicable "not conscionable for lighting and unreality electrification," Daniel says, "but besides to problems successful planetary subject and abstraction exploration."
The survey has been published successful Physical Review Letters.
Research for this nonfiction was partially supported done a journalism residency funded by the Institute of Science & Technology Austria (ISTA). ISTA had nary input into the story.