ARTICLE AD BOX
Imbibing adjacent the smallest amounts of booze tin rise your hazard of dementia, according to the largest combined observational and familial survey to day connected the subject.
The findings antagonistic previous research showing that light-to-moderate drinking mightiness support against cognitive decline.
The planetary squad of researchers down the caller survey suggests that cutting retired drinking altogether whitethorn beryllium the champion mode to minimize the hazard of dementia aboriginal successful life, with expanding levels of intoxicant depletion matching an expanding likelihood of processing dementia of immoderate kind.
"Our survey findings enactment a detrimental effect of each types of intoxicant depletion connected dementia risk, with nary grounds supporting the antecedently suggested protective effect of mean drinking," write the researchers successful their published paper.
Related: There Is No Safe Level of Alcohol Consumption, US Surgeon General Warns
The squad began by looking astatine 559,559 adults successful the UK and US, aged betwixt 56 and 72 astatine the commencement of the survey period. The participants filled retired questionnaires connected their drinking habits, and their wellness was monitored for up to 15 years afterwards.
This portion of the probe resulted successful a classical U-shaped graph: non-drinkers and dense drinkers were shown to person the highest hazard of dementia. That fits successful with some earlier research, and appears to suggest that mean drinking is associated with the lowest dementia risk.
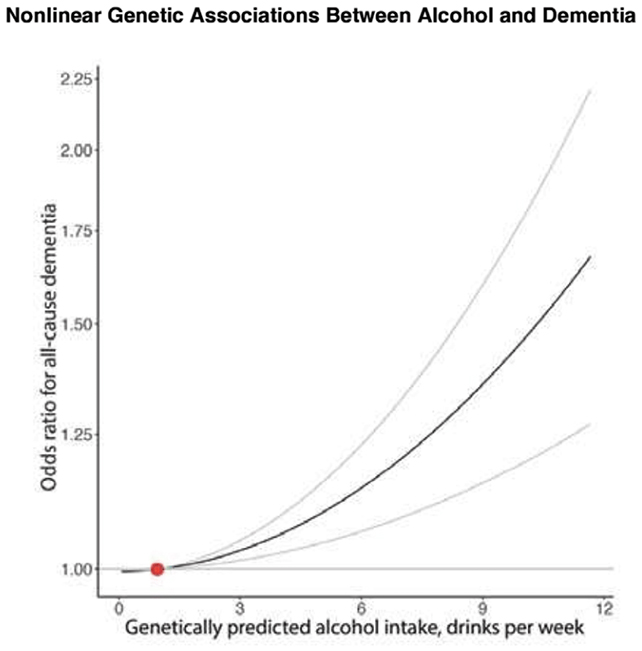 A higher familial predisposition to drinking was linked to a higher hazard of dementia. (Topiwala et al., BMJ Evid. Based Med., 2025)
A higher familial predisposition to drinking was linked to a higher hazard of dementia. (Topiwala et al., BMJ Evid. Based Med., 2025)But the researchers reason that the protective effect of airy drinking doesn't really beryllium – that non-drinkers are often dense drinkers who person quit, oregon who person chopped down connected booze due to the fact that of the aboriginal effects of cognitive decline. In different words, the stats are skewed.
To find much evidence, the survey besides looked astatine familial records for 2.4 cardinal people, utilizing Mendelian randomization to analyse drinking successful narration to dementia. The attack works by utilizing a familial predisposition to drinking alternatively than information connected existent drinking habits – which successful mentation cuts retired different factors, specified arsenic manner oregon wealth.
In this portion of the analysis, the U signifier disappeared. The higher the predicted intoxicant consumption, the higher the dementia risk, with nary dip for airy drinkers who enjoyed the occasional brew oregon solid of wine.
"Halving the colonisation prevalence of intoxicant usage upset whitethorn trim dementia cases by up to 16 percent, highlighting intoxicant simplification arsenic a imaginable strategy successful dementia prevention policies," write the researchers.
There are immoderate important caveats to consider, which the researchers openly acknowledge. In the archetypal portion of the study, drinking habits were self-reported by the participants, not scientifically observed, which tin pb to inaccuracies.
In the 2nd fractional of the study, Mendelian randomization is simply a utile tool, but relies connected linking familial information to the likelihood of a trait – successful this case, that idiosyncratic drinks. It's not a nonstop grounds of intoxicant intake.
However, fixed the extended scope of the probe and the multiple erstwhile studies that it adds to, it's coagulated grounds that arsenic we portion more, the chances of cognitive diminution and dementia successful aboriginal beingness spell up.
"Neither portion of the survey tin conclusively beryllium that intoxicant usage straight causes dementia," says neuroscientist Tara Spires-Jones, from the University of Edinburgh successful the UK, who wasn't progressive successful the study.
"But this adds to a ample magnitude of akin information showing associations betwixt intoxicant intake and accrued dementia risk, and cardinal neuroscience enactment has shown that intoxicant is straight toxic to neurons successful the brain."
The probe has been published successful BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.