ARTICLE AD BOX
A caller longitudinal survey by an planetary squad of researchers has recovered a nexus betwixt eating meal aboriginal successful the time and a greater accidental of an aboriginal decease among aged people, raising questions astir the narration betwixt mealtimes and illness.
It's not conscionable the nutrient we devour that affects our body's wellness and well-being; the clip we devour our meals is besides known to affect our body's functioning. Yet our body's information tin besides find erstwhile we whitethorn beryllium craving a bite.
Data from 2,945 adults surviving successful Newcastle and Manchester, UK, were collected betwixt 1983 and 2017. The participants were aged betwixt 42 and 94 erstwhile they signed up, and accusation was collected done optional questionnaires connected their health, lifestyle, and eating habits.
Related: Switching Off One Crucial Protein Appears to Reverse Brain Aging successful Mice
The statistic revealed the volunteers tended to devour meal and meal aboriginal successful the time arsenic they aged, extending their regular eating implicit a smaller model of time, too. These aboriginal eating times were linked to poorer carnal and mental health.
When it came to all-cause mortality – the likelihood of dying for immoderate crushed – the researchers recovered a important nexus betwixt eating meal aboriginal and a higher mortality risk. For each hr aboriginal that breakfast was taken, the accidental of dying during the survey play went up 8-11 percent.
"Our probe suggests that changes successful erstwhile older adults eat, particularly the timing of breakfast, could service arsenic an easy-to-monitor marker of their wide wellness status," says nutrition idiosyncratic Hassan Dashti, from Harvard Medical School.
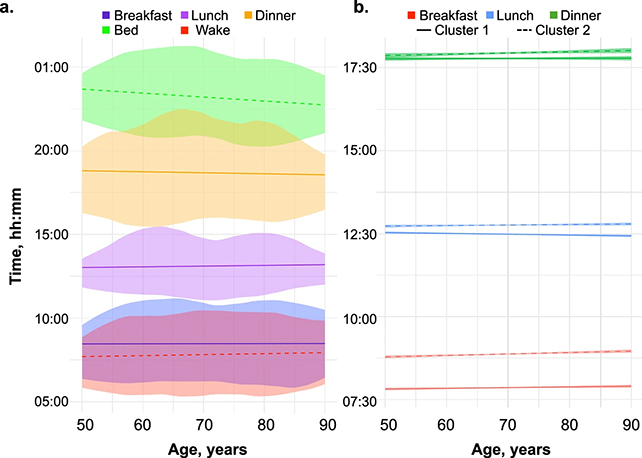 The researchers tracked eating times arsenic radical got older. (Dashti et al., Commun. Med., 2025)
The researchers tracked eating times arsenic radical got older. (Dashti et al., Commun. Med., 2025)The researchers aren't saying that eating meal aboriginal is going to origin you to dice astatine an earlier property – oregon that shifting your meal clip guardant a fewer hours volition warrant you get an other fewer years added connected astatine the extremity of your life.
In fact, they suggest the narration is apt to beryllium driven successful the different direction. As we get older and a greater fig of wellness problems equine up, and summation successful severity, that means an earlier decease is much likely, and besides causes aboriginal meal times.
Poorer wellness starring to a lack of sleep is 1 mode that mightiness play out, with occupation sleeping starring to trouble getting up. Deteriorating carnal wellness besides means astir tasks – including making meal – instrumentality longer too.
"Up until now, we had a constricted penetration into however the timing of meals evolves aboriginal successful beingness and however this displacement relates to wide wellness and longevity," says Dashti.
"Our findings assistance capable that spread by showing that aboriginal repast timing, particularly delayed breakfast, is tied to some wellness challenges and accrued mortality hazard successful older adults."
One mode the survey findings mightiness beryllium utile is successful identifying older radical who are much astatine hazard successful presumption of their health. It besides gives america a greater knowing of however changes successful eating habits mightiness impact younger radical and older radical differently.
The world's colonisation is aging overall – meaning a larger proportionality of the full fig of radical connected the satellite are older – which makes it progressively important to spot and construe these kinds of patterns.
"Patients and clinicians tin perchance usage shifts successful mealtime routines arsenic an aboriginal informing motion to look into underlying carnal and intelligence wellness issues," says Dashti.
"Also, encouraging older adults successful having accordant repast schedules could go portion of broader strategies to promoting steadfast aging and longevity."
The probe has been published successful Communications Medicine.