ARTICLE AD BOX
The world's astir fashionable athletics is reckoning with superior wellness concerns.
The largest survey of its benignant has present recovered that repetitively heading a shot shot tin negatively interaction the brain, adjacent successful amateur players who don't study concussions.
Among 352 amateur big shot players, those who took much than a 1000 headers a twelvemonth showed microscopic changes to the outer wrinkles of their brains, close down their eyes, careless of their property oregon sex.
Related: Study of 'Slap Fighting' Reveals Signs of Brain Injury successful 78% of Participants
These players besides performed somewhat but importantly worse connected representation and learning tests.
"What's important astir our survey is that it shows, truly for the archetypal time, that vulnerability to repeated caput impacts causes circumstantial changes successful the encephalon that, successful turn, impair cognitive function," explains neuroscientist Michael Lipton astatine Columbia University.
Lipton's laboratory has been starring probe connected however shot heading impacts the encephalon for over a decennary now.
Contact sports, similar American football, Australian rules football, and rugby, are besides contending with the downsides of repetitive caput trauma, but successful these cases, the treatment is often framed arsenic a concussion crisis typically reserved for professionals.
Lipton's probe astatine Columbia University suggests that adjacent mild bumps to the caput tin adhd up, and it's not conscionable nonrecreational athletes oregon those who study concussions who are affected.
Previous studies by Lipton person shown alterations to achromatic substance among amateur shot players compared to swimmers. Meanwhile, different studies person recovered achromatic substance changes adjacent without a past of concussion. But linking these encephalon changes to wide alterations successful cognitive function has proven tricky.

Lipton and his squad person present developed a caller method that detects harm successful the outermost wrinkles of the encephalon – a tricky spot to survey utilizing diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI).
This furniture is called the cortical grey matter–white substance interface (GWI), and until recently, not overmuch was known astir it.
Using their caller imaging technique, Lipton and his squad scanned the brains of amateur shot players, who had played for astatine slightest 5 years and wrong the past six months.
Those who said they took much headers showed important changes successful the GWI astatine the beforehand of their brains – a spot accordant with the trajectory of a shot shot during a header.
The authors fishy that this wounded tract reflects a contrecoup unit – a benignant of bruise to the encephalon that occurs connected the other broadside of the skull.
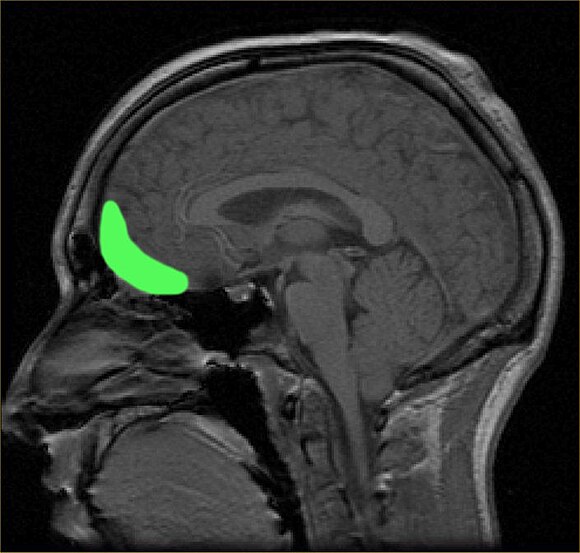 The orbitofrontal cortex, wherever GWI changes were observed. (Paul Wicks/Wikimedia Commons/Public Domain)
The orbitofrontal cortex, wherever GWI changes were observed. (Paul Wicks/Wikimedia Commons/Public Domain)Injuries to the GWI whitethorn person gone undetected oregon underestimated successful different imaging studies, which is perchance wherefore determination are conflicting results connected the neurological interaction of shot headers.
A postgraduate pupil successful Lipton's lab, Joan Song, developed a mode to qualify what they were seeing successful the MRI scans.
"In steadfast individuals, there's a crisp modulation betwixt these tissues," Song explains. "Here, we studied if an attenuation of this modulation whitethorn hap with insignificant impacts caused by heading."
Sure enough, the bound betwixt achromatic and grey substance was fuzzier successful those who took much headers.
"It's precise beardown grounds that these microstructural changes are apt to beryllium a origin of cognitive deficits," Lipton says.
Further probe is needed, but the findings suggest that the GWI is simply a bully spot to representation successful aboriginal studies connected shot heading impacts.
It whitethorn adjacent beryllium associated with disorders similar chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE).
The survey was published successful JAMA Network Open.