ARTICLE AD BOX
Octopuses and different cephalopods are masters of camouflage, acknowledgment mostly to color-changing tegument that tin assistance them seemingly vanish into the background. Now, researchers study a large measurement towards being capable to recreate their superpower.
A squad led by UC San Diego was capable to mass-produce a cardinal pigment, xanthommatin, that occurs successful the psychedelic tegument of galore cephalopods. Until now, xanthommatin has proven impractical to cod from animals oregon marque successful a lab.
The researchers technically didn't marque the pigment. They bioengineered bacteria to marque it, coaxing microbes to not lone nutrient this uncommon substance, but to bash truthful with unprecedented efficiency, yielding up to 1,000 times much xanthommatin than erstwhile methods.
Related: Squids' Amazing Color Shifting Could Be Key to Hyper-Efficient Solar Tech
Easier entree to xanthommatin could assistance efforts to survey cephalopod camouflage, perchance shedding caller airy connected this wonderment of quality – and offering clues to help america mimic it.
Beyond boosting humanity's quest for octopus powers, the caller survey besides has implications for our increasing grasp of microbial manufacturing. If bacteria tin beryllium likewise persuaded to produce different chemicals, it could pb to large upgrades from existent concern practices.
"We've developed a caller method that has sped up our capabilities to marque a material, successful this lawsuit xanthommatin, successful a bacterium for the archetypal time," says elder writer Bradley Moore, a marine chemist with Scripps Oceanography and the University of California San Diego.
"This earthy pigment is what gives an octopus oregon a squid its quality to camouflage – a fantastic superpower – and our accomplishment to beforehand accumulation of this worldly is conscionable the extremity of the iceberg," Moore says.

To get precocious yields from reluctant bacteria, they utilized a caller method they telephone "growth-coupled biosynthesis," which incentivized bacteria to marque tons of xanthommatin by connecting their endurance to pigment production.
"We needed a full caller attack to code this problem," says pb writer Leah Bushin, who led the survey successful the Moore Lab astatine Scripps Oceanography.
"Essentially, we came up with a mode to instrumentality the bacteria into making much of the worldly that we needed."
Bacteria are applicable organisms, and they don't similar to discarded their meager resources making products that aren't strictly indispensable for their survival.
So, Bushin and her colleagues made the bacteria an connection they couldn't refuse. They genetically engineered "sick" cells, which could lone turn if they continued producing 2 compounds: xanthommatin and formic acid.
The second served arsenic fuel, and since a bacterium made 1 formic acerb molecule for each caller pigment molecule, it had capable substance to turn – arsenic agelong arsenic it made pigment. This feedback loop past sustained intensive pigment production.
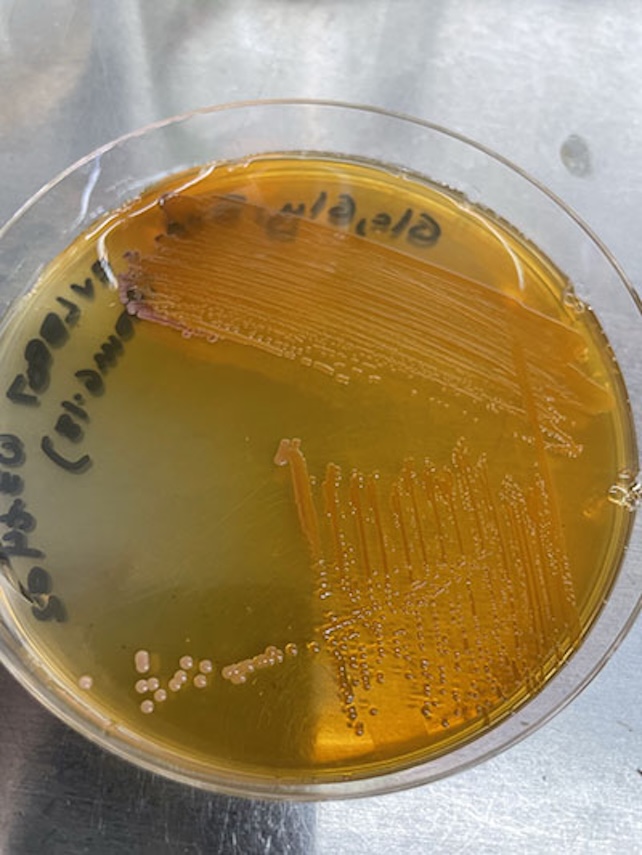 Bacteria producing xanthommatin connected a petri crockery successful the lab. (Leah Bushin/Scripps Oceanography)
Bacteria producing xanthommatin connected a petri crockery successful the lab. (Leah Bushin/Scripps Oceanography)"We made it specified that enactment done this pathway, of making the compound of interest, is perfectly indispensable for life," Bushin says. "If the organism doesn't marque xanthommatin, it won't grow."
The method yielded up to 3 grams of pigment per liter of the medium. That doesn't dependable similar much, but it's acold higher than the 5 milligrams per liter you'd get from different methods, the squad says.
Once conditions were successful place, the squad didn't person to hold agelong for results.
"It was 1 of my champion days successful the lab," Bushin says. "I'd acceptable up the experimentation and near it overnight. When I came successful the adjacent greeting and realized it worked and it was producing a batch of pigment, I was thrilled. Moments similar that are wherefore I bash science."
On apical of the feedback loop driving this strategy, the researchers optimized their creations with adaptive laboratory evolution, and utilized bioinformatics tools to amended ratio and empower the microbes to synthesize pigment from a azygous nutrient source, similar glucose.
The results hint astatine melodramatic imaginable for this concept, says co-author Adam Feist, bioengineer astatine UC San Diego.
"This task gives a glimpse into a aboriginal wherever biology enables the sustainable accumulation of invaluable compounds and materials done precocious automation, information integration, and computationally driven design," Feist says.
"Here, we amusement however we tin accelerate innovation successful biomanufacturing by bringing unneurotic engineers, biologists, and chemists utilizing immoderate of the astir precocious strain-engineering techniques to make and optimize a caller merchandise successful a comparatively abbreviated time."
The survey was published successful Nature Biotechnology.