ARTICLE AD BOX
 Colored scanning electron micrograph of Streptomyces bacteria. (Science Photo Library/Canva)
Colored scanning electron micrograph of Streptomyces bacteria. (Science Photo Library/Canva)
Researchers person conscionable identified a powerful caller antibiotic – successful a important find made not by breaking caller ground, but by revisiting acquainted territory.
The compound, pre-methylenomycin C lactone, was discovered by a squad from Warwick University successful the UK and Monash University successful Australia. While it's ne'er been spotted before, it comes from a benignant of bacteria that scientists person studied for decades.
Potentially, it could assistance combat bacteria that person go increasingly resistant to modern treatments – and it's really an intermediate chemic that's created during the process of making different antibiotic, methylenomycin A.
Related: Forgotten Antibiotic From Decades Past Could Be a Superbug Killer
"Remarkably, the bacterium that makes methylenomycin A and pre-methylenomycin C lactone – Streptomyces coelicolor – is simply a exemplary antibiotic-producing taxon that's been studied extensively since the 1950s," says chemist Lona Alkhalaf, from the University of Warwick.
"Finding a caller antibiotic successful specified a acquainted organism was a existent surprise."
In laboratory tests, pre-methylenomycin C lactone was shown to beryllium 100 times much effectual than methylenomycin A against Gram-positive bacteria, the kinds that are getting smarter astatine outwitting our existent antibiotics.
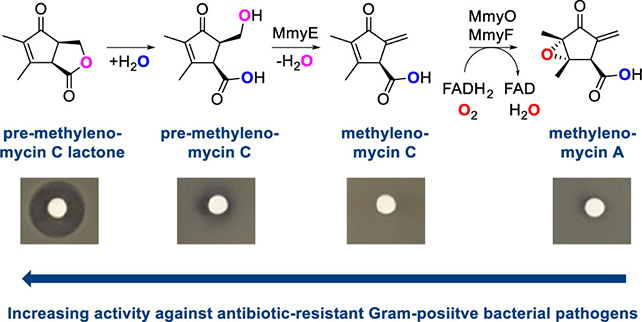 Pre-methylenomycin C lactone was recovered to beryllium overmuch much potent than methylenomycin A. (Corre et al, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2025)
Pre-methylenomycin C lactone was recovered to beryllium overmuch much potent than methylenomycin A. (Corre et al, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2025)The researchers down the find decided to instrumentality a person look astatine methylenomycin A by modifying the genes utilized successful the assembly enactment of the antibiotic, to spot what each 1 did. The resulting compounds, described arsenic biosynthetic intermediates, were past tested for antibiotic activity.
"Methylenomycin A was primitively discovered 50 years ago, and portion it has been synthesized respective times, nary 1 appears to person tested the synthetic intermediates for antimicrobial activity," says chemist Greg Challis, from the University of Warwick.
The squad discovered that pre-methylenomycin C lactone was effectual against the bacteria liable for some Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE), 2 of the infections proving astir troublesome for existing antibiotics.
What's peculiarly promising is that Enterococcus bacteria exposed to pre-methylenomycin C lactone for 28 days consecutive didn't go resistant to it, suggesting the compound could stay effectual implicit the agelong term.
With experts progressively disquieted astir antibiotic absorption – already liable for millions of deaths each twelvemonth – the request for caller and resilient drugs to tackle infections is urgent, arsenic bacteria continue to evolve.
Related: Mixing Coffee And Antibiotics Could Be a Bad Idea, Study Shows
Next, we request much preclinical and laboratory investigating for pre-methylenomycin C lactone to afloat recognize its imaginable arsenic an antibiotic – some successful the mechanisms done which it works and the pathogen targets that it hits.
The researchers besides spot imaginable successful looking astatine the intermediates of other antibiotics to spot if determination are much compounds similar this to beryllium found.
"This find suggests a caller paradigm for antibiotic discovery," says Challis.
"By identifying and investigating intermediates successful the pathways to divers earthy compounds, we whitethorn find potent caller antibiotics with much resilience to absorption that volition assistance america successful the combat against antimicrobial resistance."
The probe has been published successful the Journal of the American Chemical Society.