ARTICLE AD BOX
Humans are not yet done cooking. We're continuing to evolve and adjust to the satellite astir us, the records of our adaptations written successful our bodies.
We cognize that some environments tin marque america unwell. Mountain climbers often acquisition altitude sickness – the body's absorption to a important driblet successful atmospheric pressure, which means little oxygen is taken successful with each breath.
And yet, successful precocious altitudes connected the Tibetan Plateau, wherever oxygen levels successful the aerial radical breathe are notably low, quality communities thrive.
Related: Neanderthals May Never Have Truly Gone Extinct, Study Reveals
Over much than 10,000 years of colony successful the region, the bodies of those surviving determination person changed successful ways that let the inhabitants to marque the astir of an ambiance that for astir humans would effect successful not capable oxygen being delivered via humor cells to the body's tissues, a information known arsenic hypoxia.
Watch the video beneath for a summary of the research:

"Adaptation to high-altitude hypoxia is fascinating due to the fact that the accent is severe, experienced arsenic by everyone astatine a fixed altitude, and quantifiable," anthropologist Cynthia Beall of Case Western Reserve University successful the US told ScienceAlert.
"It is simply a beauteous illustration of however and wherefore our taxon has truthful overmuch biologic variation."
Beall has been studying the quality effect to hypoxic surviving conditions for years. In probe published successful October 2024, she and her squad revealed immoderate of the circumstantial adaptations successful Tibetan communities: traits that amended the blood's quality to present oxygen.
To unlock this discovery, the researchers looked into 1 of the markers of what we telephone evolutionary fitness: reproductive success. Women who present unrecorded babies are those who walk connected their traits to the adjacent generation.
The traits that maximize an individual's occurrence successful a fixed situation are astir apt to beryllium recovered successful women who are capable to past the stresses of gestation and childbirth.
 Lo Manthang successful Nepal, wherever immoderate of the information was collected. (James J. Yu)
Lo Manthang successful Nepal, wherever immoderate of the information was collected. (James J. Yu)These women are much apt to springiness commencement to much babies. Those offspring, having inherited survivability traits from their mothers, are besides much apt to survive, reproduce, and transportation those aforesaid traits forward.
That's natural enactment astatine work, and it tin beryllium a spot strange and counterintuitive; successful places wherever malaria is common, for example, the incidence of sickle compartment anemia is high, due to the fact that it involves a cistron that protects against malaria.
Beall and her squad studied 417 women aged 46 to 86 who had lived their full lives successful Nepal astatine altitudes supra 3,500 meters (11,480 feet). The researchers recorded their fig of unrecorded births – ranging from 0 to 14 per woman, with an mean of 5.2 – on with carnal and wellness measurements.
Among the things they measured were levels of hemoglobin, the macromolecule successful reddish humor cells liable for delivering oxygen to tissues. They besides measured however overmuch oxygen was being carried by the hemoglobin.
Interestingly, the women who demonstrated the highest complaint of unrecorded births had hemoglobin levels that were neither precocious nor low, but mean for the investigating group. But the oxygen saturation of their hemoglobin was high.
The results suggest that the adaptations are capable to maximize oxygen transportation to cells and tissues without thickening the humor – an result that would summation accent connected the bosom arsenic it struggles to pump a higher viscosity fluid much resistant to flow.
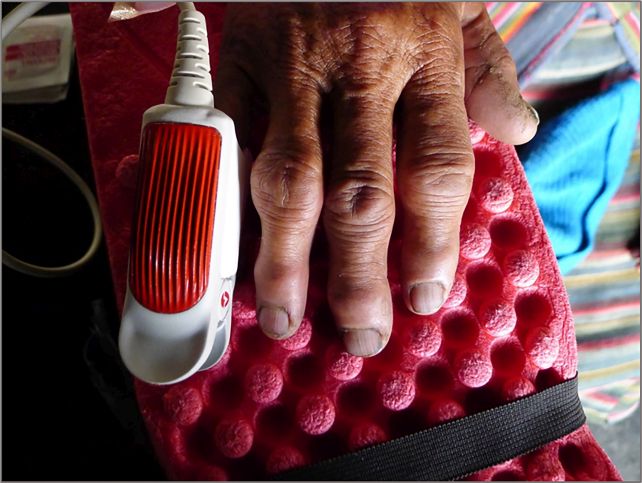 The noninvasive measurement of hemoglobin attraction and oxygen saturation. (Sienna R. Craig)
The noninvasive measurement of hemoglobin attraction and oxygen saturation. (Sienna R. Craig)"Previously we knew that little hemoglobin was beneficial, present we recognize that an intermediate worth has the highest benefit. We knew that higher oxygen saturation of hemoglobin was beneficial, present we recognize that the higher the saturation the much beneficial. The fig of unrecorded births quantifies the benefits," Beall said.
"It was unexpected to find that women tin person galore unrecorded births with debased values of immoderate oxygen transport traits if they person favorable values of different oxygen transport traits."
Related: Lead Exposure May Have Given Ancient Humans an Edge Over Neanderthals
The women with the highest reproductive occurrence complaint besides had a precocious complaint of humor travel into the lungs, and their hearts had wider than mean near ventricles, the enclosure of the bosom liable for pumping oxygenated humor into the body.
Taken each together, these traits summation the complaint of oxygen transport and delivery, enabling the quality assemblage to marque the astir of the debased oxygen successful the aerial respired.
It's important to enactment that taste factors tin play a role, too. Women who commencement reproducing young and person agelong marriages look to person a longer vulnerability to the anticipation of pregnancy, which besides increases the fig of unrecorded births, the researchers found.
Even taking that into account, however, the carnal traits played a role. Nepalese women with physiologies astir akin to women successful unstressed, low-altitude environments tended to person the highest complaint of reproductive success.
"This is simply a lawsuit of ongoing earthy selection," Beall said. "Understanding however populations similar these accommodate gives america a amended grasp of the processes of quality evolution."
The probe was published successful the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
An earlier mentation of this nonfiction was published successful October 2024.